A devastating magnitude-7.8 earthquake rocked Nepal. It was so powerful that tremors were felt in north and east India. Near the quake epicentre, two similar disasters were recorded in the recent times. In 1988, a magnitude-6.9 earthquake claimed more than 1500 lives. The 1934 quake, 8 on Richter scale, was worse. More than 10,600 people lost their lives. Why do earthquakes hit the Himalayan area so often? Well, nature is unpredictable. It is still impossible to predict such adversities. However, science can answer a few basic questions.
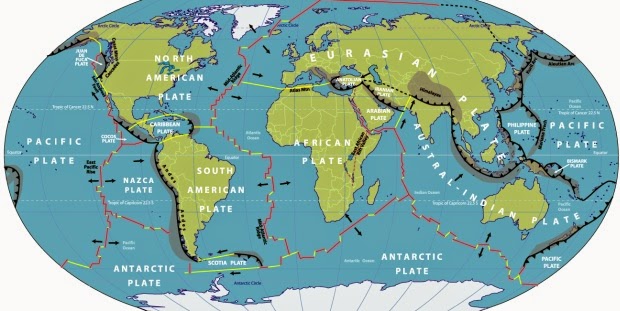
To find out the cause of earthquakes in the Himalayan region, we first need to understand our planet. The outermost shell of the Earth is made of multiple tectonic plates. These plates have been reported to move about 10 cm a year. Too slow for us humans, but quite swift in a planet's life.
Oftentimes, these plate movements drive landmasses to collide. This can cause incredible amount of pressure. One such event gave rise to the world's highest mountain range. And that's the Himalayas mountain range for us.
According to USGS (US Geological Society), about a 225 million years ago India was located near Australia. Thanks to the plate movements, India travelled over 6400 km to crash into Eurasia about a 55 million years ago. This resulted in the rise of the Himalayas. The process continues — the mountain range is still growing taller as we speak.
Nepal is located near boundary between the Eurasian and Indo-Australian plate tectonics. Obviously, there's immense pressure where these two plates meet. Every once in a while, the stress releases in the form of vibrations. It's unfortunate, but true that such activities will continue for years to come in this beautiful country.
On a related note, Japan is the most luckless nation when it comes to plate tectonics. It sits on a junction to Pacific plate, North American plate, Philippine sea plate, and Eurasian plate. Hence, it is battered by massive quakes.
-Source http://www.techtree.com/content/features/8871/understanding-why-himalayan-region-prone-earthquakes.html#sthash.FKOR06xN.dpuf

Comments
Post a Comment